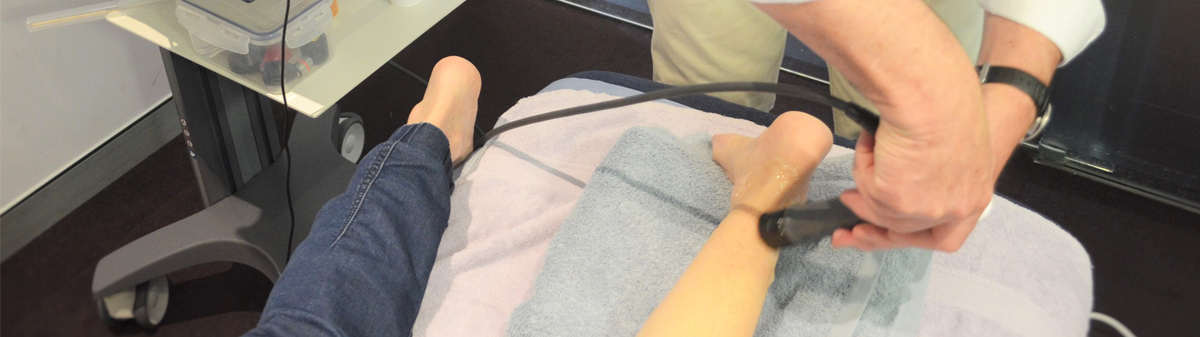
ESWT
What is extracorporeal shockwave therapy?
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a relatively new treatment with growing applications in physiotherapy, orthopaedics, urology, aesthetics and cardiology.
The machine releases high-amplitude pulses of mechanical energy produced by an electromagnetic coil. As these pass through the skin, they are converted into mechanical energy (sound waves), which travel through tissue and trigger certain biological effects.
How does it work?
The resulting microtrauma to the cells promotes catabolic and inflammatory reactions that stimulate wound healing. ESWT also promotes a process in blood vessels and nerve cells, called angiogenesis and neurogenesis respectively.
ESWT therapy is increasingly being used to treat an array of conditions and symptoms relating to muscles, tendons, bones and joints.
ESWT is not invasive as the shockwaves are applied externally to the body, and any side effects are normally mild and transient.
What are the benefits of shockwave?
- It’s an innovative, evidence-based therapy that has been shown to successfully treat various conditions. It is safe, economical and effective in bringing about pain relief and improved function (Carulli et al, 2016, Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology)
- The machine treats causes rather than just symptoms
- A 2015 systematic review in the American Journal of Sports Medicine found moderate evidence indicating ESWT therapy is more effective than the current best practice for several specific conditions. It was found to be more effective than exercises and corticosteroid for greater trochanteric pain syndrome, more effective than eccentric loading for insertional achilles tendinopathy (but equally effective for mid portion achilles) with moderate evidence to support that combining ESWT with eccentric loading produces superior results. There was also limited evidence to support ESWT being more effective in the treatment of patella tendinopathy than current non-operative treatments (Mani-Babu et al, 2015, The effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in lower limb tendinopathy: a systematic review)
- It increases and speeds up long-term tissue healing and pain reduction without medication and invasive therapies
- It has minimal recorded side-effects (namely, possible bruising or mild swelling and redness)
- It may offer an effective alternative to surgical treatment
- Patients can return to sports, daily activities and work after a few days without pain
When it might help
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy can be applied to a range of conditions and symptoms including:
- Rotator cuff tendinopathy and tears
- Heel pain (calcaneal spurs)
- Bone healing and necrosis
- Plantar fasciitis
- Achilles tendinopathy
- Patella tendinopathy
- Tennis/golfer’s elbow
- Foot ulcers in diabetic patients
- Chronic neck/back pain with trigger points
- General muscle tension (trigger point)
- ITB Friction Syndrome
- Hamstrings tendinopathy
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome
- Other insertional tendinopathy